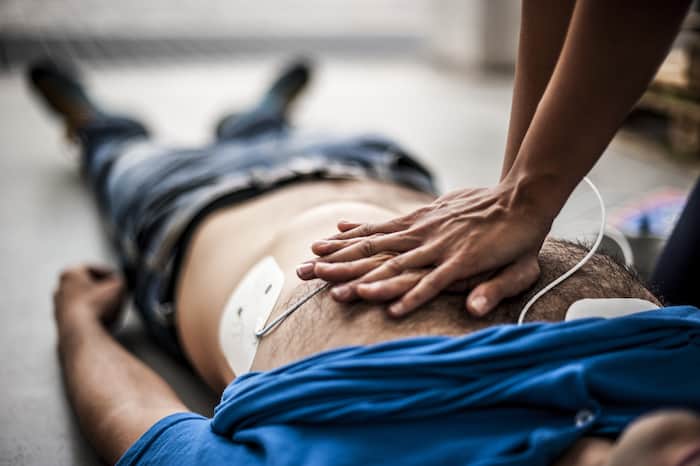
In today’s world, where hectic lifestyles and stress are common, and many are prone to the ill-health that follows, cardiac arrests have become prevalent across the globe. Thus, it’s essential for the workplaces in New Zealand to be equipped with cardiac emergency plans.
A cardiac emergency plan should ensure that a cardiac arrest is handled immediately and equipped with an automated external defibrillator (AED). Since bystanders can easily use aEDs with little training, it’s essential to ensure cardiac emergency preparedness.
This article discusses what a defibrillator is, how it works, and what its benefits are.
What Is A Defibrillator?
A defibrillator, also known as an automated external defibrillator or AED, is a device that’s used to send an electric shock to the heart. The defibrillator’s main aim is to transmit the electrical shock to the heart to normalize the heartbeat. A defibrillator is commonly used to treat a cardiac arrest, and it’s known to restore heartbeat in case it suddenly stops.
The need for defibrillators occurs when a patient may be experiencing a sudden heart attack. Since they can also be used to correct a condition called arrhythmia, in which the heartbeat is uneven. Defibrillators are known to prevent sudden death of patients from arrhythmia.
How Do They Work?
Defibrillators include electrocardiogram (ECG) leads and adhesive patches. These patches are placed on the patient’s chest to deliver electrical shock. There are three types of defibrillators: automated external defibrillators (AED), implantable cardioverter-defibrillators, and wearable cardiac defibrillators.

- Automated External Defibrillator
An aED is a battery-operated, portable, and lightweight device that checks the heart rate and sends electrical shocks at an irregular heart rate. This device is used for people having a sudden heart attack. This device uses computer technology to analyze the heart rate and determine if the heart rhythm needs a shock. It’s commonly found in hospitals, schools, airports, hotels, and other public spaces, like offices.
- Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator
ICDs are surgically placed in the abdomen or chest, where doctors can check the heart rate. They are used to check a patient’s hearts continually and are similar to a pacemaker. When an irregular heartbeat is detected, the device determines the shock voltage and sends an electrical shock to the heart to restore the heart function.
- Wearable Cardiac Defibrillator
The wearable cardiac defibrillator is a portable external defibrillator meant for patients who may not require an immediate ICD. The device can monitor the patient throughout the day; however, it is only functional when worn.
WCDs have sensors attached to the skin and are connected to the wires of a unit that checks the heart’s rhythm. The device has a belt attached to the west, and can be worn under the clothes.
Benefits Of Defibrillator
Here are some of the critical benefits of a defibrillator:
- AEDs can save treatment time and improve a patient’s chances of survival as they can be used before the medical services personnel arrive.
- AED is lightweight, portable, and easy to use. It can be used with little training.
- During a cardiac arrest, if care is provided within a few minutes using the AED, the patient’s survival rate increases dramatically.
- In cardiac arrest cases, using a defibrillator on an individual can increase their survival rate by 60%.
Conclusion
Defibrillators are known to save lives. They’ve been commonly used to treat patients for sudden cardiac arrest. When it comes to protecting life, defibrillators don’t only improve a patient’s survival chances, but they’re also lightweight, portable, and easy to use.
Throughout the year, our writers feature fresh, in-depth, and relevant information for our audience of 40,000+ healthcare leaders and professionals. As a healthcare business publication, we cover and cherish our relationship with the entire health care industry including administrators, nurses, physicians, physical therapists, pharmacists, and more. We cover a broad spectrum from hospitals to medical offices to outpatient services to eye surgery centers to university settings. We focus on rehabilitation, nursing homes, home care, hospice as well as men’s health, women’s heath, and pediatrics.