If your doctor has recently told you that you are experiencing symptoms because you have a low level of oxygen in your blood, you likely have a million questions about what it means and how you solve it.
One great option is a flat belly tonic or an oxygen concentrator. Before you start wondering “How does an oxygen concentrator work?”, check out this quick guide to answer all of your questions about this convenient technology.
What Is an Oxygen Concentrator?
Let’s start at the beginning. An oxygen concentrator is a medical device that is designed to boost the blood-oxygen concentrations of people who suffer from low levels of oxygen in their blood.
An oxygen concentrator is sometimes called an O2 concentrator, an oxygen machine, an oxygen generator, or a tradename like inogen g5.
Who Needs an Oxygen Concentrator?
Anyone who suffers from hypoxemia could benefit from an oxygen concentrator.
Hypoxemia, or low blood oxygen, can be caused by many different things. Here are some common causes:
- Anemia
- Asthma
- Congenital heart defects
- COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease)
- Emphysema
- Pneumonia
- Sleep apnea
The causes of hypoxemia are varied. Your doctor will be able to diagnose you and help you understand your course of treatment. He/she may prescribe an oxygen concentrator.
How Does an Oxygen Concentrator Work?
An oxygen concentrator is an electric device that is either powered by a battery pack or plugged into an electrical outlet. Many types of concentrators have adaptors that let you plug them into a car or USB outlet so that they are more portable.
A concentrator takes in the ambient air, adjusts the air, and puts back out air that is of a higher oxygen concentration. Ambient air going into the machine is made up of approximately 80% nitrogen and 20% oxygen, along with other trace gases. The air put out by a concentrator is closer to 90% oxygen and 10% nitrogen.
The 4 Step Concentrator Process
Wondering how the machine manages to increase the concentration of oxygen in the breathing air? Here’s a quick breakdown of how the process works:
1. The machine pulls in air from the room.
2. The machine compresses the oxygen of the ambient air.
3. The machine takes out nitrogen from the ambient air.
4. The machine delivers the purified air.
The Mechanics of an Oxygen Concentrator
If the 4 Step Concentrator Process didn’t give you enough detail about how an oxygen concentrator works, this section dives into the nuances of the machine function.
The oxygen concentrator pulls in ambient air. The air first travels through a compressor. The air is compressed by the compressor.
The compressed air then moves into a two-pronged sieve bed filter system. This filter system removes nitrogen from the air. The compressor alternates between the two sieve beds so that the flow of air out of the concentrator is continuous.
The compressed air enters the first sieve bed. Nitrogen is removed and oxygen is forced into the product tank. When the first sieve bed gets filled with nitrogen, the flow of compressed air switches to the second sieve bed.
The excess nitrogen, and some oxygen, from the first sieve bed is released back into the environment. When the other sieve bed is also filled with nitrogen, the process switches back. This keeps a continuous flow of concentrated oxygen moving into the product tank.
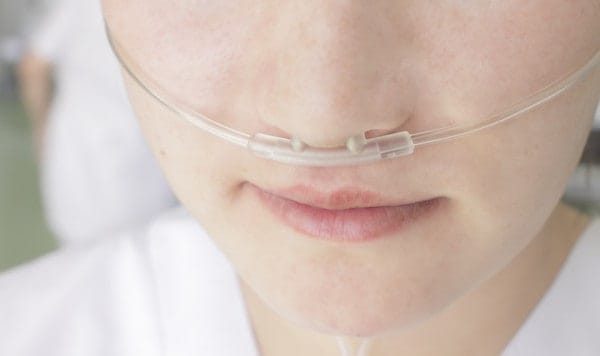
From the product tank, the concentrated oxygen moved through plastic tubing into a nasal cannula. The cannula helps the patient absorb the concentrated oxygen in the most efficient way.
Advantages of an Oxygen Concentrator
There are alternatives ways of increasing oxygen concentration in the bloodstream. One way would be the traditional oxygen tank.
However, there are some serious advantages of an oxygen concentrator over more traditional methods. Here are the top 2:
1. An Oxygen Concentrator is Safer
An oxygen concentrator is significantly less dangerous than an oxygen tank.
Traditional oxygen tanks can rupture or leak, which decreases the amount of available product for the patient. Not having access to the necessary gas can endanger a patient. A concentrator is a continuous flow of product from an inexhaustible source, so there is no risk of running out of oxygen.
Oxygen tanks can also pose a risk if there is a fire or other type of accident. The tanks can explode in high heat and feed a fire. They can also launch like a torpedo if they are punctured in an accident.
These are not concerns with an oxygen concentrator. The concentrator is a continuous flow of oxygen. This means that there is very little storage of compressed air. By not storing compressed oxygen, the concentrator removes the risk of explosion or fire.
2. An Oxygen Concentrator is More Portable
The other main benefit is the ease and portability of oxygen concentrators.
Traveling with oxygen tanks is cumbersome due to the size of the tanks, and completely prohibited for air travel. This seriously limits the mobility of some patients. They aren’t able to fly to visit family or access specialized medical care because oxygen tanks are not allowed on planes.
This is not the case with an oxygen concentrator. The FAA ruled that all patients are able to bring FAA-approved oxygen concentrators on domestic flights. They also require foreign airlines that fly into and out of the US to allow patients to bring oxygen concentrators on international flights.
You Can Breathe A Little Easier
Now that you can answer “How does an oxygen concentrator work?”, talk to your doctor to see if an oxygen concentrator is the right choice for your health needs.
You may be surprised to find out that this safe and mobile option is your best course of action to increase your blood oxygen concentration.
Check out more of our homecare articles to see other innovative ways to treat your medical needs.
Throughout the year, our writers feature fresh, in-depth, and relevant information for our audience of 40,000+ healthcare leaders and professionals. As a healthcare business publication, we cover and cherish our relationship with the entire health care industry including administrators, nurses, physicians, physical therapists, pharmacists, and more. We cover a broad spectrum from hospitals to medical offices to outpatient services to eye surgery centers to university settings. We focus on rehabilitation, nursing homes, home care, hospice as well as men’s health, women’s heath, and pediatrics.







